Show More
Symptoms
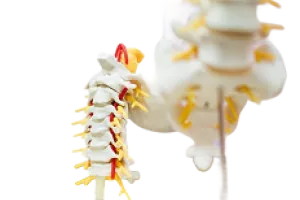
Some spinal cord vascular malformations are congenital, while others develop later in life. Symptoms may appear suddenly (acutely) or develop gradually over several years. Common symptoms include:
Loss of sensation or abnormal sensations such as numbness or tingling
Sudden onset of pain in the back, neck, or legs
Extreme weakness in the upper or lower extremities
Loss of bladder and bowel control
Progressive neurological deficits
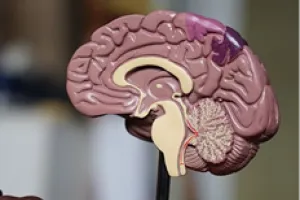
Headache
Neck stiffness
Photosensitivity (intolerance to bright light)
Paralysis
Pain radiating down the leg
Loss of sensation or abnormal sensations such as numbness or tingling
Sudden onset of pain in the back, neck, or legs
Extreme weakness in the upper or lower extremities
Loss of bladder and bowel control
Progressive neurological deficits
Headache
Neck stiffness
Photosensitivity (intolerance to bright light)
Paralysis
Pain radiating down the leg
Treatments
Treatments
Medications may help manage symptoms such as seizures, headaches and back pain.
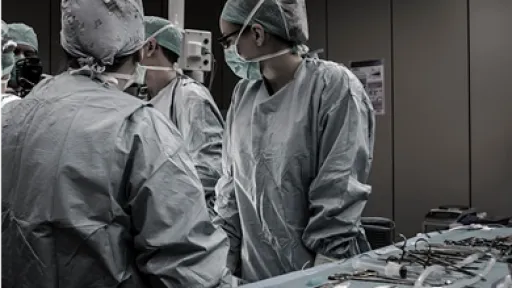
Surgery
The main treatment for AVM is surgery. Specific doctor might recommend surgery if you're at a high risk of bleeding. The surgery might completely remove the AVM. This treatment is usually used when the AVM is in an area where surgeon can remove the AVM with little risk of causing significant damage to the brain tissues.
Endovascular embolization is the type of surgery in which the surgeon threads a catheter through the arteries to the AVM. A substance is injected to nearest parts of the AVM to reduce the blood flow. This might also be done before brain surgery or radiosurgery to help reduce the risk of complications.
Sometime the stereotactic radiosurgery is used to treat AVMs. It uses intense, highly focused beams of radiation to damage the blood vessels and stop the blood supply to the AVM.
Medications may help manage symptoms such as seizures, headaches and back pain.
Surgery
The main treatment for AVM is surgery. Specific doctor might recommend surgery if you're at a high risk of bleeding. The surgery might completely remove the AVM. This treatment is usually used when the AVM is in an area where surgeon can remove the AVM with little risk of causing significant damage to the brain tissues.
Endovascular embolization is the type of surgery in which the surgeon threads a catheter through the arteries to the AVM. A substance is injected to nearest parts of the AVM to reduce the blood flow. This might also be done before brain surgery or radiosurgery to help reduce the risk of complications.
Sometime the stereotactic radiosurgery is used to treat AVMs. It uses intense, highly focused beams of radiation to damage the blood vessels and stop the blood supply to the AVM.